Welcome to the world of software development, where a well-crafted software delivery plan holds the key to seamless project deployment. In this rapidly advancing landscape, having a structured approach to delivering software solutions is crucial for success. A software delivery plan acts as a guiding beacon, ensuring that development teams navigate the complexities of the project with clarity and efficiency. From defining the project scope to allocating resources and setting realistic timelines, a robust delivery plan sets the stage for a smooth and successful journey towards delivering a high-quality software product to users. Working in the technology industry offers an exciting opportunity to shape the future through the strategic planning and efficient delivery of software solutions that revolutionize how we live, work, and interact. So, let’s delve into the intricacies of a software delivery plan and unlock the secrets to achieving project excellence.
What is a Software Delivery Plan?
A software program delivery plan is a comprehensive roadmap that outlines the diverse levels worried within the software improvement and deployment technique. It serves as a guiding light for developers, project managers, and stakeholders, offering them a clear vision of the obligations to hand and the timeline for their final touch. A properly articulated plan allows for placing realistic expectations, handling dangers, and making sure of transparency throughout the project lifecycle.
Importance of Software Delivery Project Plan
Having a well-thought-out project plan is paramount to the success of any endeavour. It serves as a roadmap, guiding teams via the various levels of an assignment and making sure an established method to achieving objectives. A project plan clarifies the project’s scope, defining what wishes to be executed and putting clean desires for all involved. This clarity eliminates ambiguity, reduces misunderstandings, and fosters effective verbal exchange among team individuals and stakeholders.
Moreover, a project plan helps allocate resources efficiently, ensuring that time, manpower, and budget are utilized optimally. It allows for the identification of potential risks and challenges, enabling teams to proactively devise contingency strategies. As a result, the likelihood of project delays or failures decreases significantly.
By having a comprehensive project plan in place, teams can stay focused, organized, and on track throughout the project’s lifecycle. It empowers them to monitor progress, assess achievements, and make necessary adjustments as circumstances change. Ultimately, the project plan acts as a foundation for success, providing a structured framework for teams to deliver their best work and attain their project goals with confidence.
Why Plan and Deliver Projects?
Effective project planning and delivery are vital for successful outcomes. By following a structured approach, projects can stay on track, minimize risks, and achieve desired objectives. A well-executed project enhances productivity, fosters collaboration, and ensures efficient resource allocation.
What is Project Planning and Delivery?
Project planning involves defining project goals, scope, timelines, and resource requirements. It lays the groundwork for the project’s execution. Project delivery refers to the implementation phase, where the planned activities are executed, monitored, and controlled to reach the project’s desired endpoint.
Key Components of a Software Delivery Plan
1. Project Scope and Objectives:
The first step in crafting a successful software delivery plan is defining the project’s scope and objectives. Understanding the desired outcomes and the problem the software aims to solve is crucial for setting the right direction and aligning all team members towards a common goal.
2. Task Breakdown and Timeline:
A detailed task breakdown is essential for effective project management. Divide the project into smaller, manageable tasks and assign them to respective team members. Alongside task allocation, establish realistic timelines to avoid bottlenecks and delays.
3. Resource Allocation:
Allocating the right resources to specific tasks is vital for maintaining efficiency. Identify the skills and expertise required for each task and ensure that team members are appropriately assigned to capitalize on their strengths.
4. Quality Assurance and Testing:
To ensure a flawless end product, a robust quality assurance and testing process must be incorporated into the software delivery plan. Regular testing and debugging should be scheduled to catch and rectify any issues promptly.
5. Contingency Plan:
Every software project comes with uncertainties. It’s essential to have a contingency plan in place to address unexpected challenges that may arise during development. This will help mitigate risks and ensure a smooth continuation of the project.
6. The Significance of Collaboration:
A successful software delivery plan relies heavily on effective collaboration among team members and stakeholders. Regular meetings and open communication channels facilitate a shared understanding of the project’s progress, allowing for timely adjustments and decision-making.
The Process of Planning and Delivering a Project
The process of planning and delivering a project consists of 5 main stages as follows:
Do It: A Step-by-Step Approach
Here is a step-by-step approach to planning and delivering a project:
1. Define Objectives: Clearly outline project goals and deliverables.
2. Scope and Requirements: Identify what the project will encompass and define specific requirements.
3. Create a Plan: Develop a detailed project plan with timelines, tasks, and resources.
4. Assemble the Team: Gather a skilled and motivated team to execute the plan.
5. Execution: Implement the plan while tracking progress and addressing challenges.
6. Monitor and Control: Regularly assess project performance and take corrective actions as needed.
7. Completion: Deliver the project successfully, meeting all objectives.

Did It: A Successful Project Delivery
By following a structured planning and delivery process, our project achieved its intended goals. Clear objectives and a detailed project plan allowed us to stay focused and aligned with stakeholders’ expectations. Regular monitoring and proactive communication enabled us to address issues promptly, ensuring that the project remained on track.
How to Conduct Post-Project Analysis
Completing a project is a significant milestone, but the journey doesn’t end there. Conducting a thorough post-project analysis is a crucial step in the project management process. It provides valuable insights into the project’s successes, challenges, and lessons learned, empowering teams to improve future endeavours. Let’s explore a step-by-step guide on how to conduct a comprehensive post-project analysis.
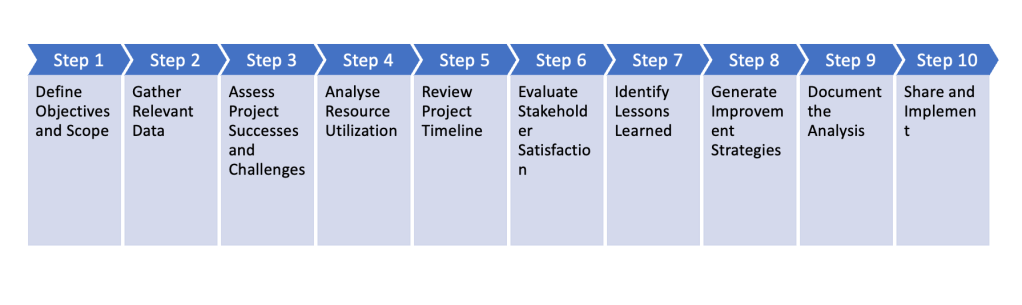
Step 1: Define Objectives and Scope
Before diving into the analysis, clearly define the objectives and scope of the post-project assessment. Outline the specific aspects you want to evaluate, such as project goals achieved, budget adherence, team performance, and overall project efficiency.
Step 2: Gather Relevant Data
Collect all relevant project data and documentation. This may include project plans, timelines, budget reports, communication records, and performance metrics. Having comprehensive data ensures an accurate and well-informed analysis.
Step 3: Assess Project Successes and Challenges
Evaluate the project’s outcomes against the defined objectives. Identify areas where the project excelled and celebrate successes. Simultaneously, identify challenges or bottlenecks faced during the project’s lifecycle.
Step 4: Analyse Resource Utilization
Examine how resources were allocated and utilized throughout the project. Assess whether there were any inefficiencies or areas where resource allocation could be optimized in future projects.
Step 5: Review Project Timeline
Analyse the project timeline and assess any delays or accelerations that occurred during execution. Understanding the factors contributing to these deviations will help streamline future scheduling.
Step 6: Evaluate Stakeholder Satisfaction
Gather feedback from key stakeholders, including clients, team members, and project sponsors. Their insights and perspectives are invaluable in understanding the project’s impact and identifying areas for improvement.
Step 7: Identify Lessons Learned
One of the most critical aspects of post-project analysis is identifying lessons learned. Encourage team members to share their experiences, challenges, and suggestions for improvement. These insights can be compiled into a lessons-learned document for future reference.
Step 8: Generate Improvement Strategies
Based on the analysis, develop strategies to address the challenges identified and capitalize on the project’s successes. Implementing these improvements in future projects can enhance efficiency and overall project outcomes.
Step 9: Document the Analysis
Record all findings, conclusions, and improvement strategies in a comprehensive post-project analysis report. This document serves as a valuable reference for future projects and allows for tracking progress over time.
Step 10: Share and Implement
Share the post-project analysis report with all relevant stakeholders, ensuring transparency and promoting a culture of continuous improvement. Implement the identified improvement strategies in subsequent projects, incorporating the lessons learned into the organization’s project management practices.
A Case study
Here’s an example of a case study in software delivery planning: After three years of work, the HP LaserJet Firmware division changed the economics of the software delivery process by adopting continuous delivery, comprehensive test automation, an iterative and adaptive approach to program management, and a more agile planning process.
In HP’s LaserJet Firmware division, a team of 400 talented individuals across the USA, Brazil, and India was responsible for developing the firmware that powered their scanners, printers, and multifunction devices. However, by 2008, they faced a significant challenge – the team was moving too slowly, and new product releases were being delayed. Their inability to deliver new features stifled innovation, leaving them to prioritize just a few ideas from the plethora brought in by marketing.
Determined to find a fresh approach, HP LaserJet leadership set ambitious targets – improve developer productivity by tenfold, take firmware off the critical path for product development, and reduce costs. To achieve these goals, they turned to continuous delivery, making significant investments in test automation, and creating a hardware simulator for virtual testing.
After three years of dedicated work, the results were astounding. The division changed the economics of software delivery, reducing overall development costs by approximately 40%, increasing programs under development by about 140%, and bringing down development costs per program by 78%. As a result, resources driving innovation multiplied eightfold.
A crucial factor in their success was the team’s substantial investment in test automation and continuous integration. Contrary to the misconception that Lean is solely about cutting costs, this transformation proved that investing to remove waste and reduce failure demand is a worker-led activity that can continuously improve quality and productivity while driving down costs.
To learn more about this remarkable case study, you can watch Gary Gruver, Director of Engineering for the FutureSmart program, presenting at FlowCon 2013 or read about the transformation in his book, “A Practical Approach to Large-Scale Agile Development: How HP Transformed LaserJet FutureSmart Firmware.” HP’s Agile transformation demonstrated the immense benefits of embracing innovative practices and investing in continuous improvement to achieve remarkable outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What should a delivery plan include?
A delivery plan should embody numerous key additives to ensure successful project implementation. It ought to include a clear definition of the task’s scope and objectives, a detailed breakdown of tasks and timelines, resource allocation, quality guarantee and trying out tactics, hazard management and a contingency plan to address unforeseen challenging situations. Additionally, powerful collaboration strategies and verbal exchange channels among crew participants and stakeholders are vital to preserving the undertaking on track.
2. What is a software delivery process?
The software program delivery technique refers to the systematic approach taken to expand and install software programs. It entails a chain of degrees, beginning from the preliminary planning and design, through coding and testing, to the very last deployment and maintenance of the software. The system can also vary depending on the improvement methodology used, such as Agile or Waterfall, but the main objective is to supply a useful and notable software program product to cease customers.
3. What is a delivery plan?
A delivery plan is a complete roadmap that outlines the steps and activities involved in handing over a project effectively. In the context of software program improvement, it refers to a plan that details the tasks, milestones, and timelines required to complete a software project and deliver the very last product to the customers. A well-established delivery plan enables manage resources, set practical expectancies, and mitigate dangers for the duration of the assignment lifecycle.
4. How do you write a project delivery plan?
Writing a project delivery plan involves several key steps:
a. Define the Project Scope: Clearly outline the project’s objectives, goals, and the problem it aims to address.
b. Break Down Tasks: Divide the project into smaller, manageable tasks and allocate them to team members based on their skills and expertise.
c. Establish Timelines: Set realistic timelines for each task and establish milestones to track progress.
d. Allocate Resources: Ensure that the right resources, including human resources and technology, are allocated appropriately to different tasks.
e. Include Quality Assurance and Testing: Incorporate a plan for quality assurance and testing to ensure a bug-free and reliable final product.
f. Manage Risks: Develop a contingency plan to address unforeseen challenges and mitigate risks that can rise throughout the undertaking.
g. Promote Collaboration: Encourage open verbal exchange and collaboration amongst group members and stakeholders to foster shared information about the project’s progress.
h. Regular Review: Periodically review and adjust the delivery plan as needed to accommodate changes or new requirements.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, a proper software delivery plan is the cornerstone of successful software program improvement and deployment. By carefully outlining the assignment’s scope, breaking down tasks, allocating sources thoughtfully, and prioritizing fine warranties, groups can navigate the complicated software improvement landscape with confidence. Effective collaboration and a contingency plan add an extra layer of resilience to the process. Remember, the journey towards a seamless software deployment begins with a robust plan!
So, in case you are venturing into a brand-new software program development venture, ensure to make investments in effort and time in creating a properly crafted software delivery plan. It will keep you heading in the right direction but additionally pave the manner for a triumphant software launch, leaving each of you and your stakeholders happy with the outcomes. Happy making plans and coding!
To learn more about creating a Software Delivery Plan , read this insightful post and learn how an SDP is more than just a roadmap; it’s a dynamic strategy that aligns technical processes with business objectives!
<This is a guest post by Indradeep Datta>
<Author Bio: Indradeep Datta, an accomplished SEO specialist and digital marketer based in London, holds an MSc in Digital Marketing. With expertise in developing successful online marketing strategies, he is also the author of the UK-based lifestyle blog, Customer Lifestyle.>